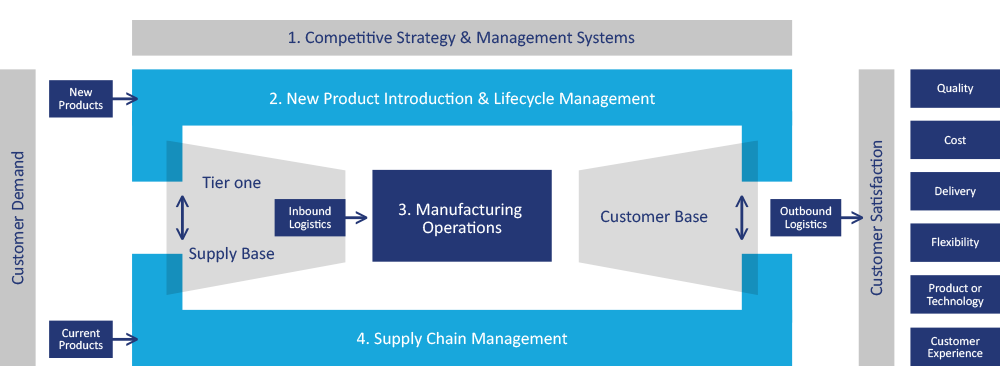
The Local Operating Environment
Competitiveness is frequently seen as a comparison between national or international operating environments. Whilst this is important to governments and multi-national companies it is rarely something that the average manufacturer can influence on their own. Joining a national trade body can magnify a company’s influence but it is still likely that the majority of their efforts will be concentrated within the Local Operating Environment.
NMCL identified a number of themes on which companies might choose to compete:
- Quality
- Cost
- Delivery
- Flexibility
- Product & Technology
- Customer experience
The Local Operating Environment demonstrates how customer demand is turned into customer satisfaction.
Within this Local Operating Environment NMCL recognised four Company Capabilities:
Competitive Strategy & Management Systems
Competitive Strategy & Management Systems are the underpinning processes, practices and tools required to drive a competitive business. It encompasses;
- Competitive strategy development and deployment
- Leadership and business planning through to the design and implementation of supporting processes
- Tools and metrics to drive business performance including international quality management systems and quality management tools.
New Product Introduction & Lifecycle Management
A cross functional process and set of activities that convert a market need into a new product that can be successfully manufactured, sold and subsequently phased out. New Product Introduction (NPI) includes the activities of programme & product management, design, development and validation, through to manufacturing, supply chain development, marketing, selling and aftersales. It is the staged process by which an entire business engages to deliver, or phase out, a product.
Manufacturing Operations
The use of labour, machines, tools, processing, or formulation to add value to material and produce a good for use or sale. It encompasses:
- The layout of people, material and equipment
- The evaluation and development of the capabilities of people and equipment
- Asset and workforce utilisation planning and management
Supply Chain Management
The combination of people, processes, systems and physical resources to balance customer demand and supply. Supply chain encompasses:
- Demand management and forecasting
- Capacity planning
- Sales and operations planning
- Orders management
- Production master scheduling, supplier scheduling, shop floor planning, inventory planning and supplier evaluation/selection/development.